Education
10 Family Secrets Hidden in Your DNA

Every family carries untold stories, and your DNA holds the key to unlocking them. Encoded within your genes are clues about your ancestry, health, and traits you might never have guessed were inherited. These genetic secrets connect generations, offering a glimpse into both the past and the future.
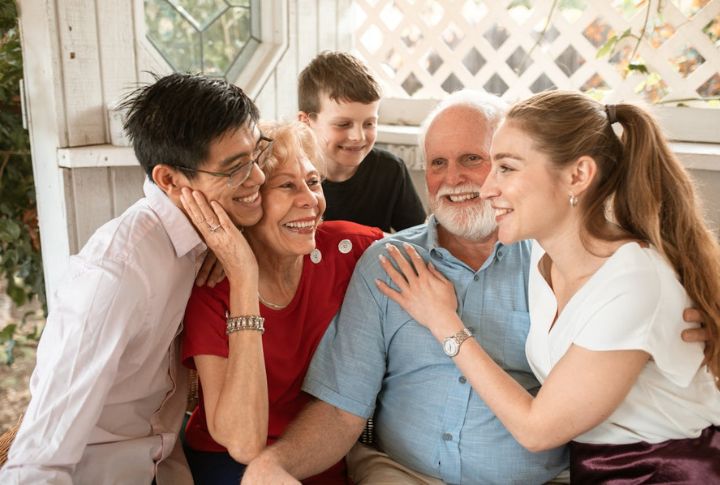
Mitochondrial DNA Carries Maternal Legacy
Mitochondrial DNA, passed solely from your mother, acts as a biological time capsule. It reveals ancient migration patterns and maternal ancestry. Scientists traced humanity’s “mitochondrial Eve,” an ancestral mother, to approximately 200,000 years ago to showcase how your maternal line connects to a shared global history.
Environmental Echoes in Epigenetic Marks

The influence of environment and lifestyle causes epigenetic changes that can leave heritable marks. Stress, diet, or even smoking can switch genes on or off and affect future generations. Famines have led to epigenetic resilience in descendants and proved that your DNA carries your story along with the stories of those before you.
Inherited Trauma’s Generational Impact

Beyond leaving emotional scars, trauma imprints itself on your DNA. Studies on Holocaust survivors reveal epigenetic changes that were linked to their descendants’ stress response. These findings demonstrate how struggles from the past can shape resilience and coping mechanisms in future generations to bridge the personal and historical.
Health Risks Stored in DNA

Your DNA serves as a map of health risks. BRCA gene mutations, for example, significantly increase cancer risks and prompt preventive screenings. Advances in personalized medicine have turned these genetic risks into actionable insights to make you take proactive steps for your well-being and your family’s protection.
Longevity Genes Shaping Your Future

Centenarians often share unique genetic variants that contribute to their extended lifespans. Genes that regulate cholesterol and inflammation, such as FOXO3A, are commonly found in families with exceptional longevity. These inherited traits underline how your DNA might hold the secret to a longer, healthier life.
Rare Mutations Influencing Generations
Silent mutations, which do not cause immediate effects, can impact future generations. For example, carriers of Tay-Sachs disease may unknowingly pass it along. Genetic testing provides an opportunity to uncover hidden mutations. This gives you a chance to mitigate risks for the next generation.
Behavioral Traits Rooted in Genes

Genetic variants shape behaviors like impulsivity, empathy, and creativity. Novelty-seeking behavior and adventurous tendencies in families are explained by a link to the DRD4 gene. Your personality is not just shaped by upbringing but by a fascinating blend of genetic inheritance and environment.
Immune Traits Passed Through Lineage

Your immune system carries traits you inherited from your ancestors who survived deadly diseases. The CCR5-Δ32 mutation, for instance, offers protection against HIV and may have safeguarded ancestors during past pandemics. These inherited quirks are living demonstrations of evolution continuing to shape our defenses.
Ancestral Traits Revealed in Features

Your physical features, like eye color and freckles, trace back to ancient mutations. Blue eyes originated from a single genetic mutation 6,000-10,000 years ago, while red hair is tied to Celtic ancestry. Small traits such as this connect you to your roots and tell the story of your lineage.
Genetic Markers of Cultural Identity

Certain DNA markers align with unique cultural heritages. For example, Native American mitochondrial haplogroups reveal migration patterns that date back thousands of years. Some genetic links emphasize how your DNA acts as a bridge between personal identity and the collective history of entire populations.