Health
10 Telltale Clues Your Sugar Intake Is Out Of Control

A quick bite of something sweet can feel like the perfect fix—until the slump hits. What seems like a pick-me-up might be behind those nagging health changes. Sugar plays a tricky game, and the signs often sneak past unnoticed. This list highlights ten common signals that your sugar intake might be way out of sync.
Constant Cravings After Eating

Feeling hungry after a full meal can signal sugar’s effect on your brain. It activates dopamine, dulls leptin—the hormone that signals fullness—and creates a loop of cravings. The more sugar you consume, the stronger the urge to keep reaching for more.
Frequent Energy Highs And Sudden Crashes

That quick jolt from a pastry won’t last. Sugar spikes blood glucose, followed by an insulin surge that crashes your energy. You’re left foggy, hungry, and dragging. Even moderate swings can resemble adrenal fatigue. These dips are a frequent culprit behind midday exhaustion.
Trouble Falling Or Staying Asleep
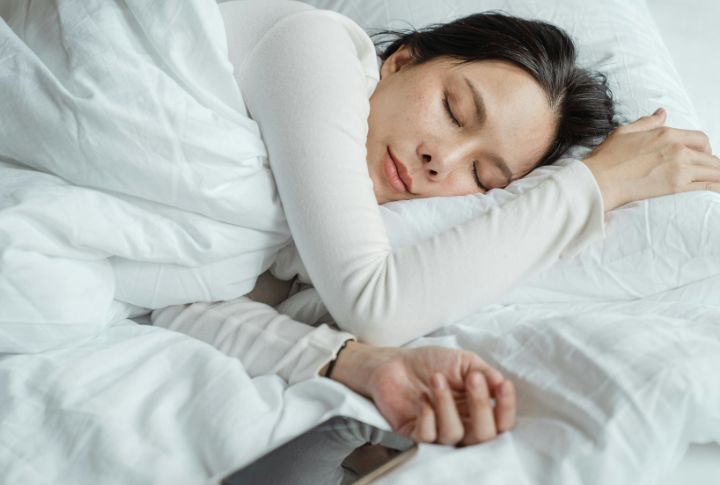

Nights get restless when sugar’s in control. Increased cortisol and adrenaline delay melatonin, the body’s sleep cue. Just one dessert can push back deep sleep by over an hour. Poor rest also worsens glucose control, creating a self-reinforcing loop of fatigue and cravings.
Skin Breakouts And Premature Wrinkles
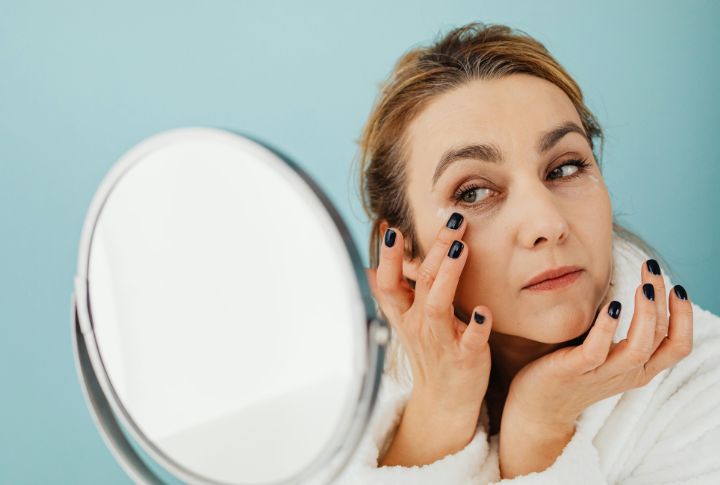

Your skin notices what your fork’s been doing. Sugar fuels glycation, which weakens collagen and elasticity. At the same time, it raises insulin, triggering more oil and clogged pores. Dermatologists link sugary diets to acne severity and faster aging—even the best creams can’t undo it.
Digestive Upset Like Bloating Or Gas
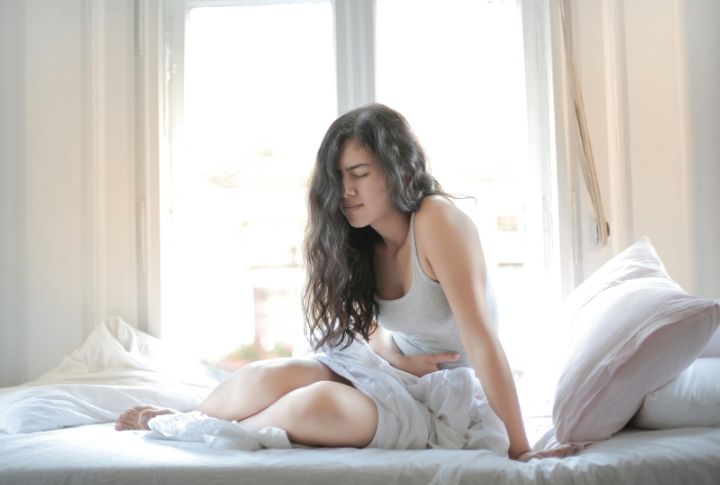

Some sugars bring more than just extra calories—they bring discomfort, too. Sugar alcohols like sorbitol ferment in the gut, often leading to bloating and gas. Even naturally sweet juices can throw digestion off. For some, sugar-free gum causes more gas than a plate full of beans.
Brain Fog Or Trouble Focusing
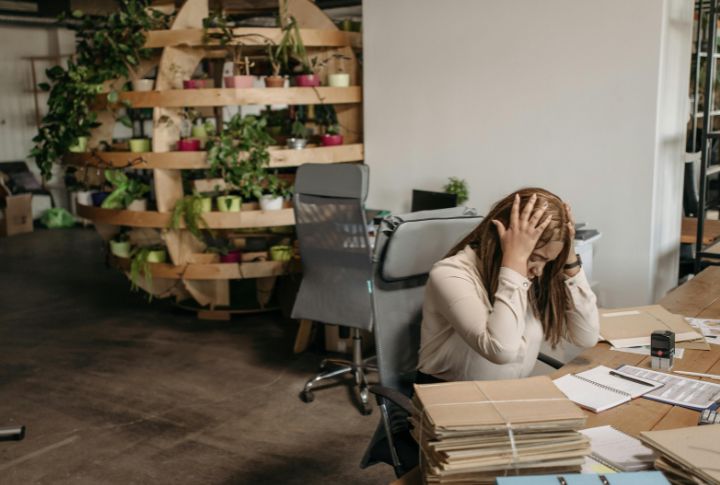

Mental sharpness takes a hit when sugar’s running the show. It inflames neural pathways and destabilizes glucose regulation, both important for memory. Just one sugary beverage can impair short-term focus. Long-term intake is linked to shrinkage in brain areas responsible for learning and recall.
Unexplained Mood Swings Or Irritability

Riding the sugar rollercoaster doesn’t just affect energy; it rattles emotions. Glucose drops mimic anxiety symptoms and reduce serotonin stability. Some researchers link sugar to depression-like patterns. In severe cases, mood shifts caused by sugar resemble early signs of mood disorders or withdrawal agitation.
Aching Joints Without Injury

Are your knees or fingers hurting out of nowhere? Sugar could be stirring up inflammation. It spikes cytokines and uric acid, both tied to stiffness and pain. Even seemingly innocent juices can aggravate arthritis. Some rheumatologists now warn patients about hidden sugars that trigger flare-ups.
Frequent Colds Or Slow Healing Wounds

Feeling under the weather more than usual? Sugar may be to blame. It weakens white blood cell function for hours and blocks vitamin C absorption. Elevated blood sugar also slows tissue repair. It is believed that a single soda can reduce immune defense by nearly half.
Noticeable Weight Gain Around The Belly

Belly fat often builds silently, and sugar is a key driver. Fructose increases visceral fat and worsens insulin resistance, especially in the midsection. Liquids like soda don’t trigger fullness cues, making it easy to overconsume. One day of consumption adds up to four pounds yearly.