Oregon
10 Facts That Make Crater Lake A Natural Wonder Like No Other
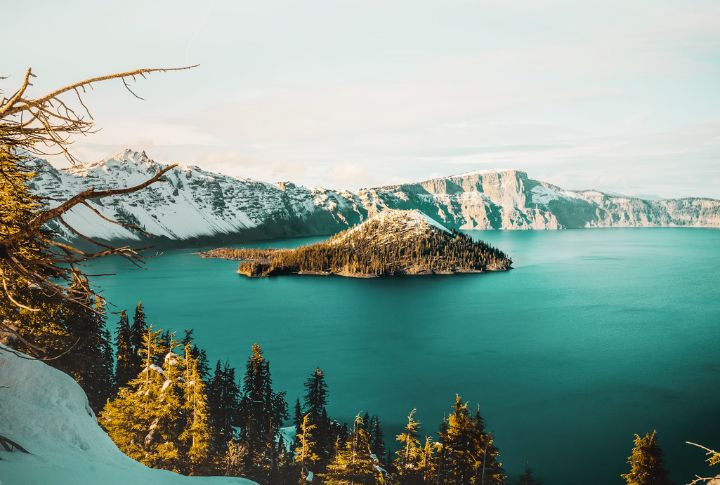

Crater Lake, situated in the Cascade Mountains of southern Oregon, draws over half a million visitors annually. However, starting in 2026, access to the lake’s shoreline will be restricted due to a rehabilitation project. This closure will last until at least 2029. So, before the access fades, uncover these 10 fascinating facts that make Crater Lake truly one of a kind.
Deepest Lake In The United States
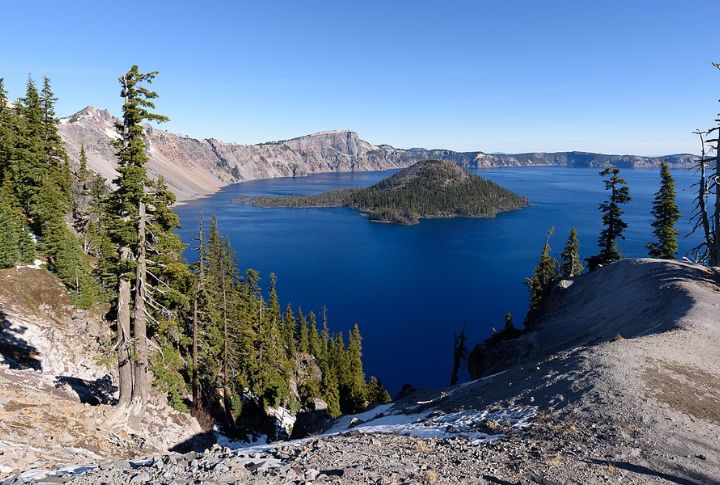

This water body reaches a maximum depth of 1,949 feet, making it the deepest lake in the United States and the deepest volcanic lake globally. Its depth was first measured in 1886 using a lead weight and piano wire and later confirmed by sonar in 1959. Its depth contributes to the mesmerizing deep blue color and exceptional clarity.
Formation
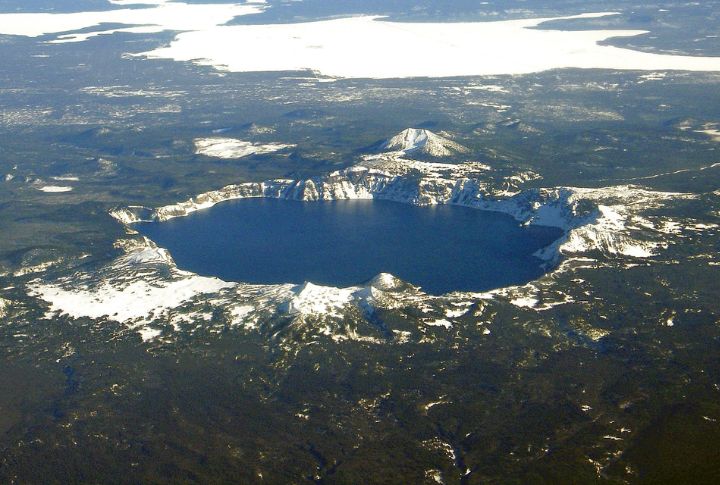

Some 7,700 years ago, Mount Mazama, a 12,000-foot-high volcano, erupted, expelling about 50 cubic kilometers of magma. This led to the collapse of the mountain’s summit and the formation of a caldera. Over time, this caldera filled with rain and snow, creating Crater Lake. Its formation is an example of a caldera lake resulting from volcanic activity.
Remarkable Water Clarity
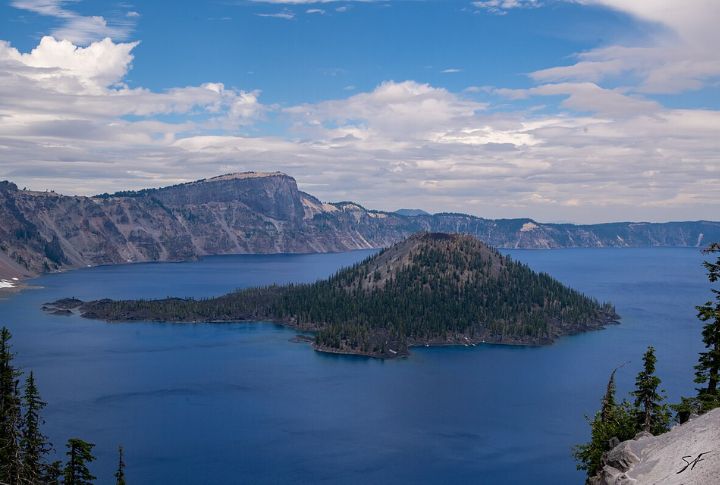

Crater Lake is known for its water clarity, with visibility often exceeding 100 feet. In 1997, a record clarity of 142 feet was observed. This clarity is due to its having no inlets or outlets, resulting in the inflow of minimal pollutants. The water’s pristine condition allows sunlight to penetrate deeply.
Unique Geological Features
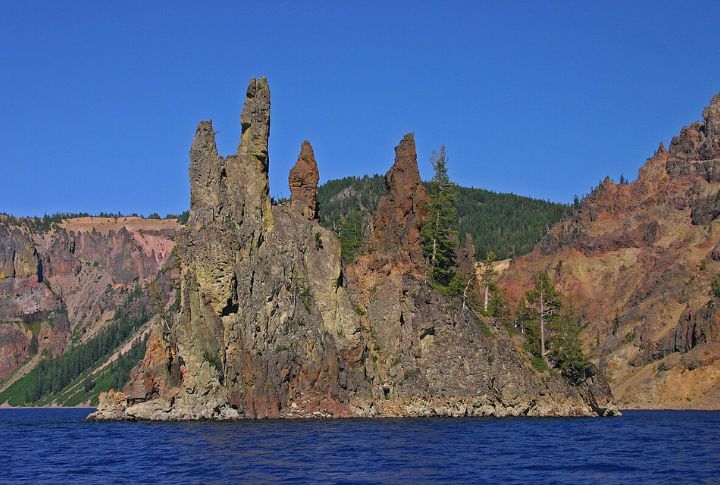

Within Crater Lake are two distinct islands, namely Wizard Island and Phantom Ship. Wizard Island is a cone-shaped landform that rises about 755 feet above the surface. It was formed by subsequent volcanic activity after the caldera’s creation. Phantom Ship is a natural rock formation resembling a small sailing ship composed of erosion-resistant lava.
Fed Solely By Precipitation
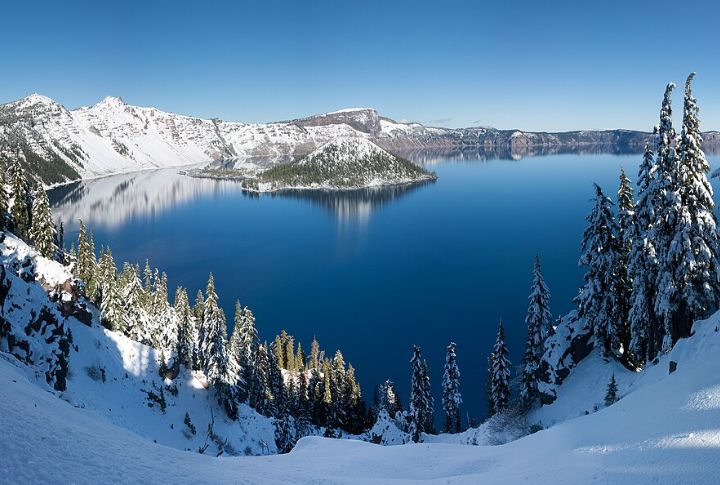

The lake has no tributaries or distributaries; it is filled with rain and snow. Its water level is maintained through precipitation, evaporation, and seepage. The absence of inflowing streams means there is little sediment or nutrient input, which limits algae growth.
Crater Lake National Park
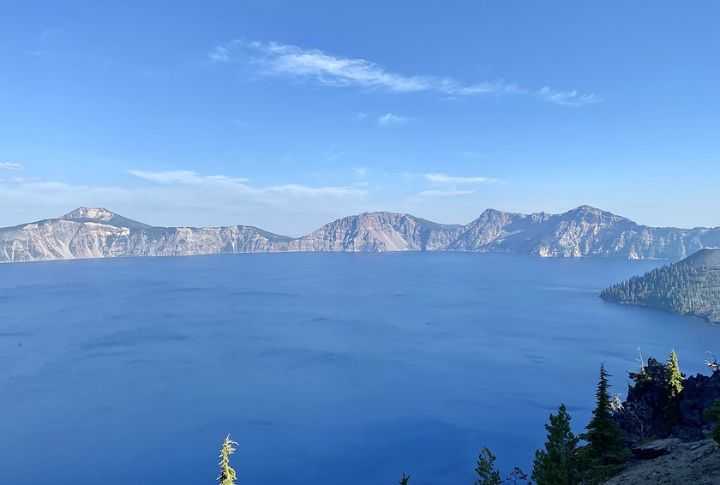

Crater Lake National Park, established on May 22, 1902, is the fifth-oldest national park in the United States. It encompasses 286 square miles of pristine wilderness, including forests and diverse wildlife. The park was created to preserve the lake’s natural beauty and geological significance. It offers various recreational activities, like hiking and camping.
Cultural Significance
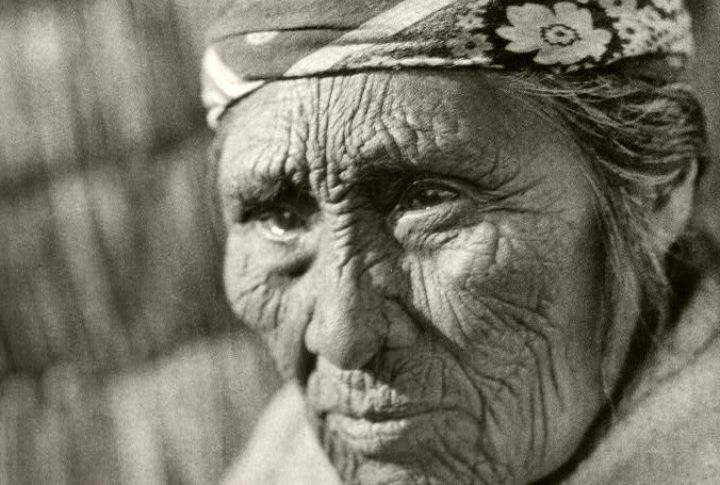

The water body holds deep spiritual significance for the Klamath Tribes, who call it “Giiwas.” According to tribal legend, Cater was created during a battle between the spirit of the sky and the spirit of the mountain. The area remains sacred, and the tribes continue to honor it through ceremonies and traditions.
Unique Ecological Features
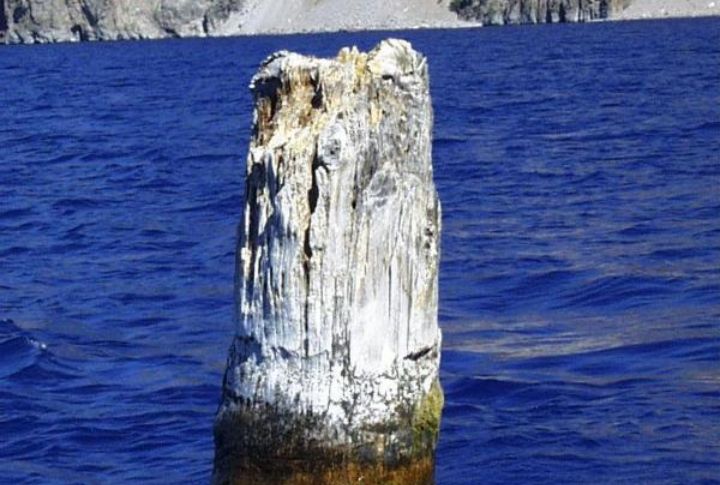

A curious feature of Crater Lake is the “Old Man of the Lake,” a 30-foot-tall tree stump that has been floating upright in the water for over a century. Its buoyancy and stability are due to the cold water slowing its decomposition. The stump travels around the lake, buoyed by wind and currents.
Crater Lake’s Climate
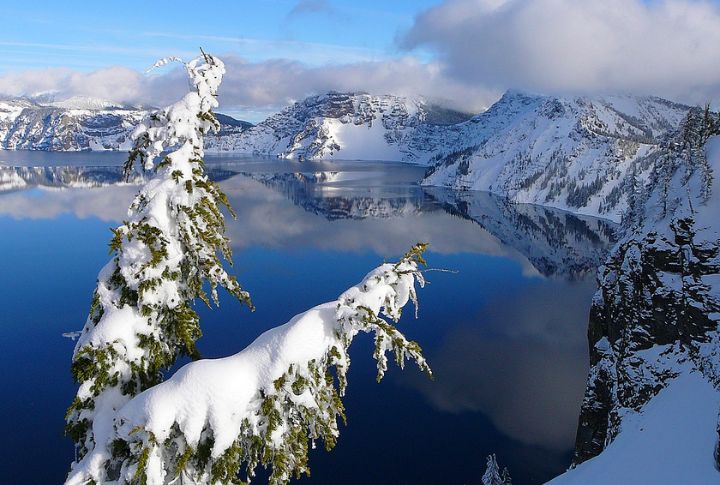

The lake experiences a unique climate characterized by long, snowy winters and short, sunny summers. Situated at the crest of the Cascade Mountains, the park receives about 42 feet of snow yearly, which makes it one of the snowiest places in America. Despite the heavy snowfall, the lake rarely freezes due to its immense depth.
Ongoing Conservation Efforts
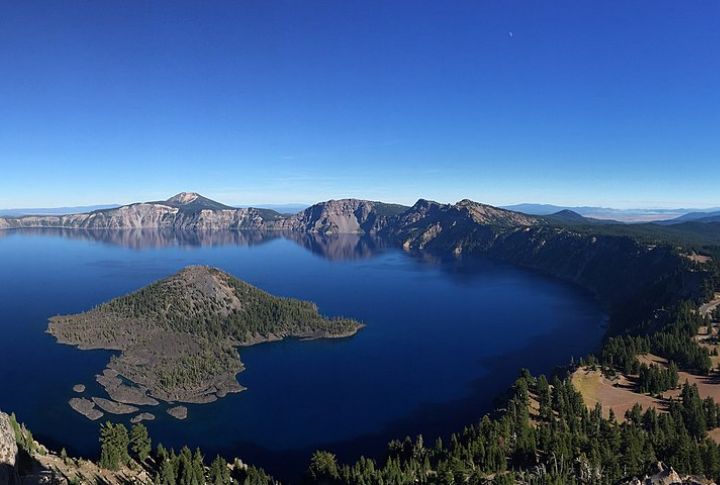

Crater Lake National Park is dedicated to preserving the lake’s natural environment and cultural heritage through active conservation efforts. Projects include forest thinning to reduce wildfire risk, invasive species control, and trail restoration to minimize erosion. The National Park Service collaborates with Native American tribes and scientists to maintain ecological balance and respect traditional practices.