Health
The Frightening Truth About Plastics In Your Brain
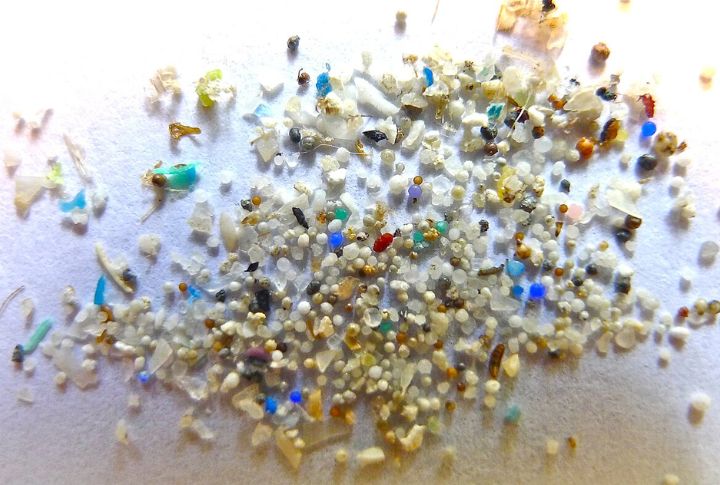

You do your best to avoid plastic waste, but what if it’s already inside you? Researchers find microplastics lodged in the human brain, sparking big questions about long-term effects. Could this silent intruder impact brain function? Understanding this issue is the first step toward protecting yourself.
Microplastics Are Now Found In Brains
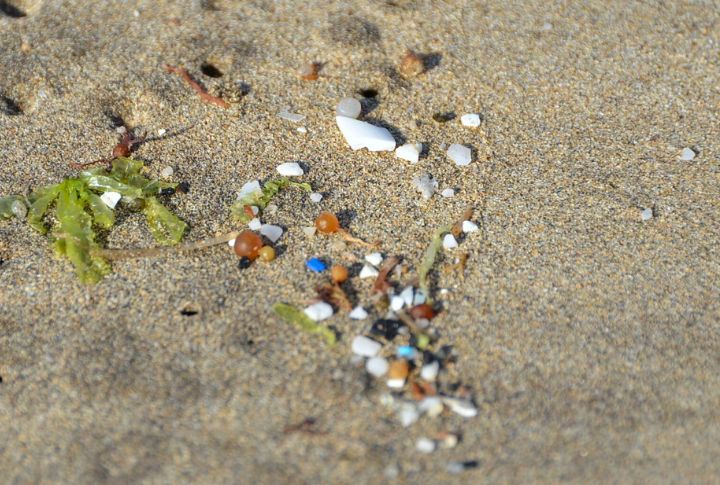

Scientific breakthroughs don’t always bring good news. Researchers discovered microscopic plastic particles in human brains, a finding that raises alarming health concerns. A 2023 study in the journal “Environmental Science & Technology” revealed nanoplastics in human brain tissue samples, proving that these materials are no longer just environmental hazards but biological contaminants.
How Plastic Particles Enter The Body
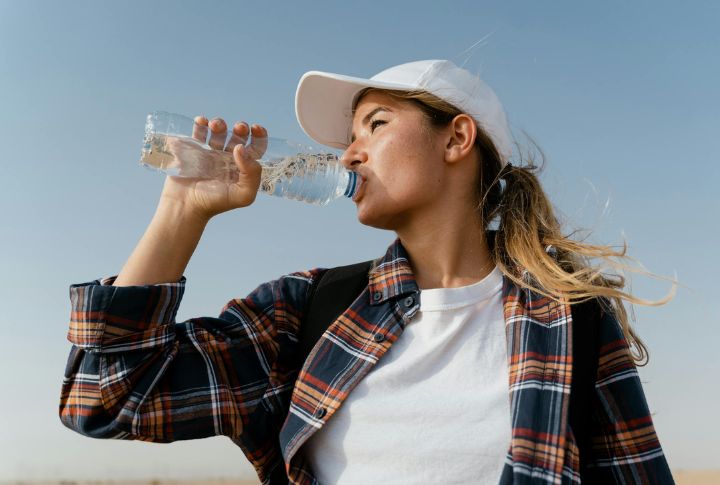

Plastic pollution isn’t just an environmental issue. Every day, you unknowingly ingest microplastics through water, food, and even the air you breathe. A study by the World Health Organization found that an average person consumes around 50,000 microplastic particles annually, with bottled water being a primary source.
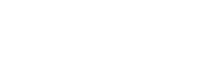
The Blood-Brain Barrier Is No Shield
A fortress isn’t much use if the enemy can slip through the gates. Microplastics have breached the blood-brain barrier. Nanoplastics are small enough to cross this critical barrier and expose delicate neural tissue to synthetic debris. This raises concerns about long-term accumulation and potential interference with brain signaling.
Plastic In The Brain May Cause Inflammation
Think of your brain like a well-oiled machine. Now, imagine throwing sand into the gears. That’s what plastic particles might be doing: triggering inflammation and possibly accelerating cognitive decline. Inflammation in the brain has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s, leading experts to question whether microplastics could be a contributing factor.
Dementia And Memory Loss Risks Increase

A study by neuroscientists at the University of Vienna reveals that plastic particles disrupt neurotransmitter activity. This interference may impair memory retention and learning abilities, raising concerns about the long-term effects of plastic exposure on cognitive health and highlighting the need for further research in this area.
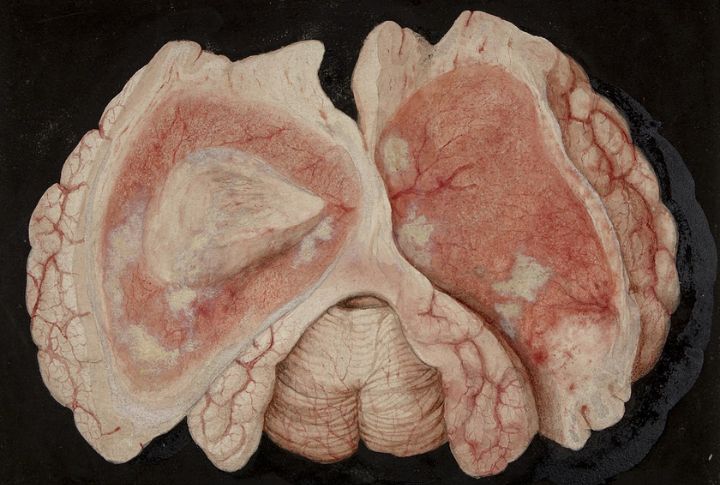
Brain Cells May Struggle To Function
Neurons are like messengers, constantly firing signals to keep your body running smoothly. But what happens when plastic gets in the way? Microplastics can interfere with cellular communication, potentially slowing processing speed and reaction time. Experiments on animal models show that prolonged exposure to nanoplastics alters neural activity and weakens synaptic connections.
Toxic Chemicals Hitch A Ride Inside
Plastic carries a cocktail of toxic chemicals, some of which have been linked to hormonal imbalances and neurological damage. Many plastics contain bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates, chemicals that disrupt endocrine function. When microplastics reach the brain, these chemicals may leach into the surrounding tissue to create risks far beyond the physical obstruction.
Sources Of Plastic You May Ingest

Not all plastic exposure is apparent. Bottled water and even table salt contain trace amounts of microplastics. Research conducted by the University of Newcastle in Australia estimates that humans ingest about the equivalent of a credit card’s worth of plastic each week. Seafood is another primary source, as marine life absorbs plastic from polluted waters.
Scientists Are Racing To Study Effects

This discovery has pushed scientists into overdrive. Researchers worldwide are studying the impact of microplastics on brain function, hoping to determine long-term effects before it’s too late. So far, the results are unsettling. Noticeably, the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences started multiple studies to understand whether these particles contribute to neurological diseases.
Ways To Reduce Your Plastic Exposure

Every small change helps. Switching to filtered tap water and using glass or stainless steel containers can limit exposure. Reducing synthetic fabric use and regularly dusting indoor spaces can lower airborne plastic intake. While eliminating plastic is impossible, minimizing daily exposure is one of the best defenses.