
Fossil-rich locations have become keys to understanding ancient ecosystems. They showcase well-preserved remains of plants and animals. The sites reveal extinct species and the environments they inhabited. Here are 20 fossil hotspots that shed light on Earth’s prehistoric past.
Dinosaur National Monument in the United States

Over 1,500 dinosaur fossils are preserved in this monumental site, which spans Colorado and Utah. These fossils, trapped in the rock layers for millions of years, offer a glimpse into a world dominated by massive sauropods and theropods.
The Burgess Shale in Canada
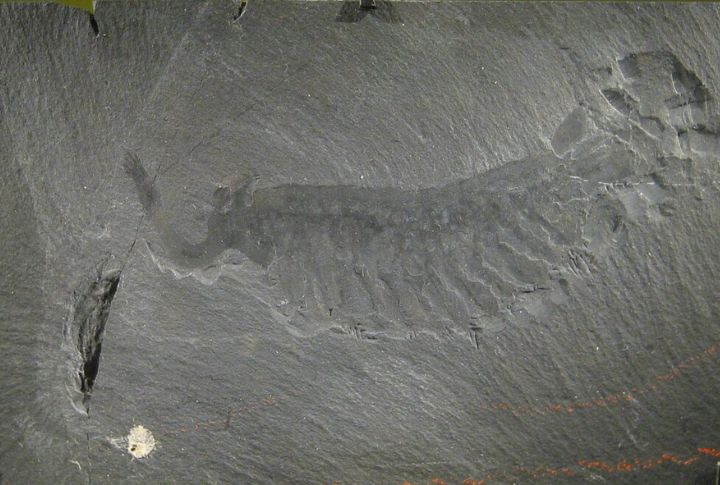

Famed for its incredible preservation of soft-bodied organisms, the Burgess Shale provides one of the most detailed snapshots of Cambrian life. This site, located in the Canadian Rockies, reveals a diverse range of creatures from over 500 million years ago.
Isle of Skye in Scotland

Jurassic dinosaur footprints preserved in the island’s rugged cliffs give invaluable insights into the movements of ancient creatures. The Isle of Skye holds traces of theropods and sauropods, giving paleontologists clues about how these dinosaurs behaved.
La Brea Tar Pits in Los Angeles
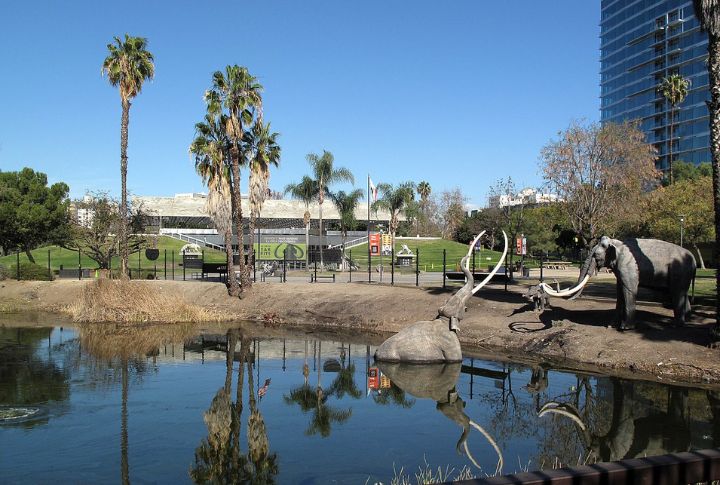

Saber-toothed cats, mammoths, and dire wolves were trapped in sticky tar for over 50,000 years, leaving behind a massive collection of Ice Age fossils. Today, the La Brea Tar Pits continue to reveal the ancient fauna of the Pleistocene.
Solnhofen Limestone in Germany
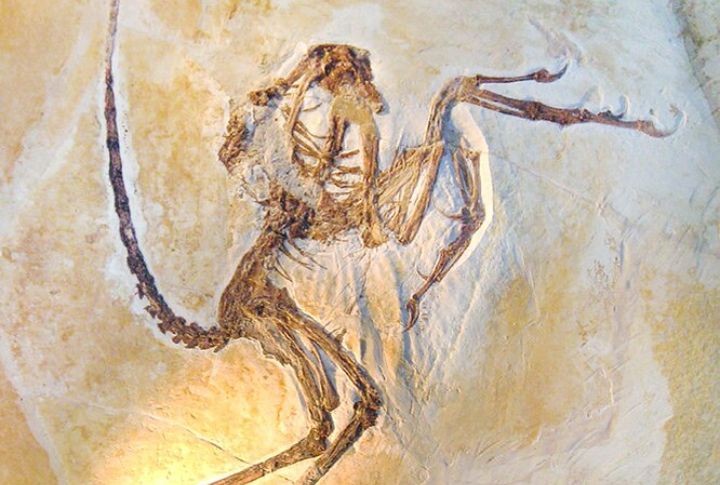

The site from the late Jurassic, preserving an extraordinary variety of fossils, including the famous Archaeopteryx, offers rare insight into the origins of flight. The fine-grained limestone captures incredible details of dinosaurs, early birds, and flying reptiles.
Yixian Formation in China

Incredible fossil discoveries from this site have changed our knowledge of the connection between dinosaurs and birds. Yixian Formation is especially famous for its feathered dinosaur fossils, some of which show preserved feathers.
Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania
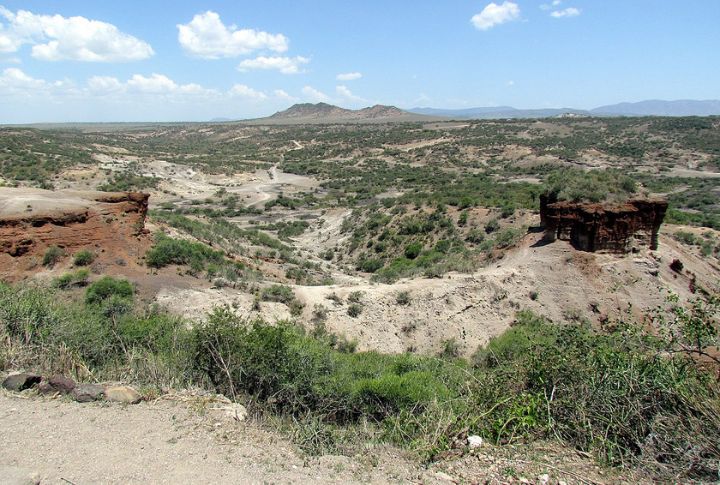

The place, known as the “Cradle of Humanity,” holds fossil evidence of early human ancestors. Dating back more than 2 million years, the fossils uncovered here have reshaped the study of human evolution and reveal essential information about early hominids.
The Messel Pit in Germany

Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage location, the Messel Pit has astonishingly well-preserved fossils from the Eocene. The fossils of early mammals, reptiles, and birds found here are often so well-preserved that soft tissues remain intact.
The Karoo Basin in South Africa
Rich in fossils from the Permian and Triassic periods, it is key to understanding early vertebrate evolution. This site offers a snapshot of life before and after the Permian elimination, showcasing the diversity of early reptiles and the first ancestors of modern mammals.
Liaoning Province in China
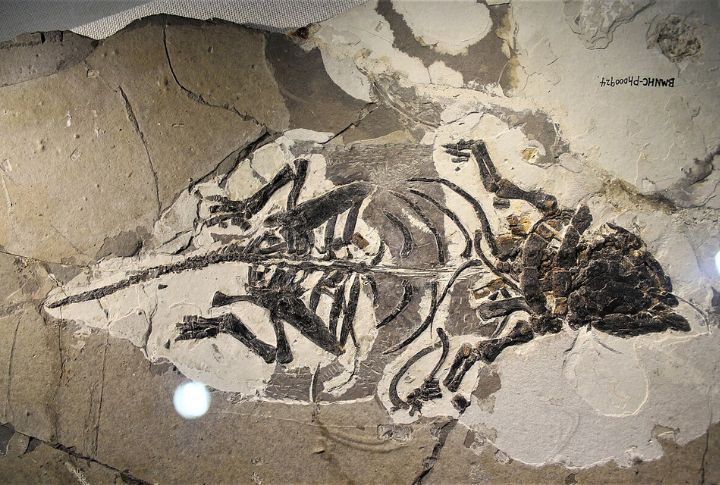

Liaoning’s Early Cretaceous fossils bridge the gap between dinosaurs and birds. The site is famous for preserving fossils of feathered dinosaurs. These discoveries have deepened the understanding of avian origins and the development of feathers.
Green River Formation in Wyoming

The Green River Formation, a Miocene fossil hotspot, preserves ancient freshwater ecosystems from 50 million years ago. Its exceptional fossils of fish, insects, and plants offer invaluable insights into prehistoric life and ecosystem evolution.
The Sahara Desert in Africa

Today’s arid Sahara was once home to a thriving ecosystem, evidenced by fossils of ancient fish, crocodiles, and dinosaurs. These fossils reveal a dramatically different climate and environment, which provides essential clues about the Sahara’s lush prehistoric past.
Mazon Creek in Illinois
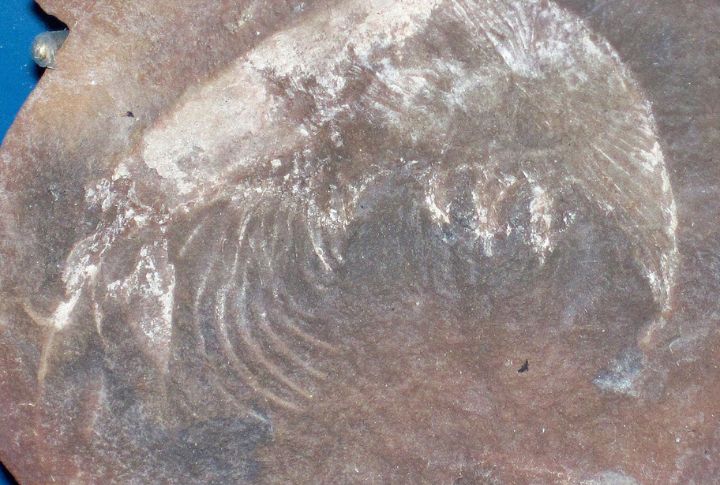

Mazon Creek, a Carboniferous-era site, holds well-preserved fossils of land and marine life. Unique fossil beds reveal ancient swamp ecosystems, providing paleontologists with an exceptional record of plants, insects, and aquatic creatures that thrived millions of years ago.
Czech Republic’s Czech Caves

The Moravian region caves are filled with Pleistocene-era fossils, including remains of Neanderthals and megafauna. These fossils offer insights into human and animal life in Ice Age Europe to help scientists track the migration and behavior of early humans and their environment.
The Winton Formation in Australia

In Queensland, the Winton Formation holds an impressive collection of Cretaceous fossils, including large sauropods and theropods. This site is key to understanding prehistoric Australian ecosystems and offers vital information on the diversity of dinosaur life that roamed the continent.
Pinnacle Point Caves in South Africa
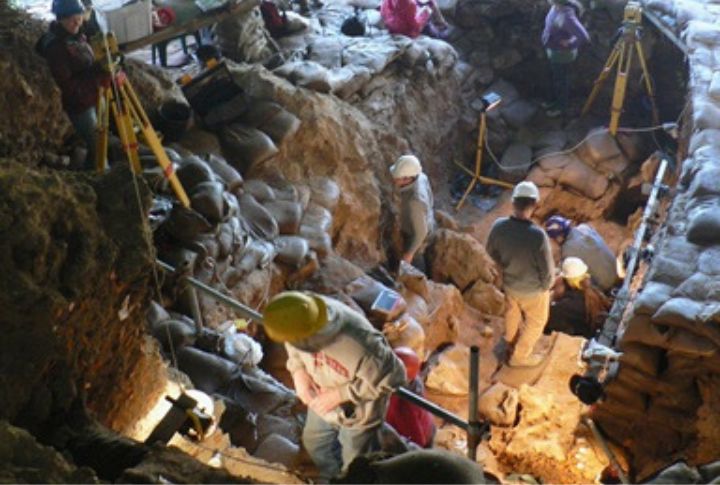

These caves contain some of the earliest evidence of Homo sapiens, with fossils revealing the use of tools and other behaviors. Dating back 160,000 years, the Pinnacle Point Caves provide essential clues on human evolution and migration patterns.
The Gobi Desert in Mongolia
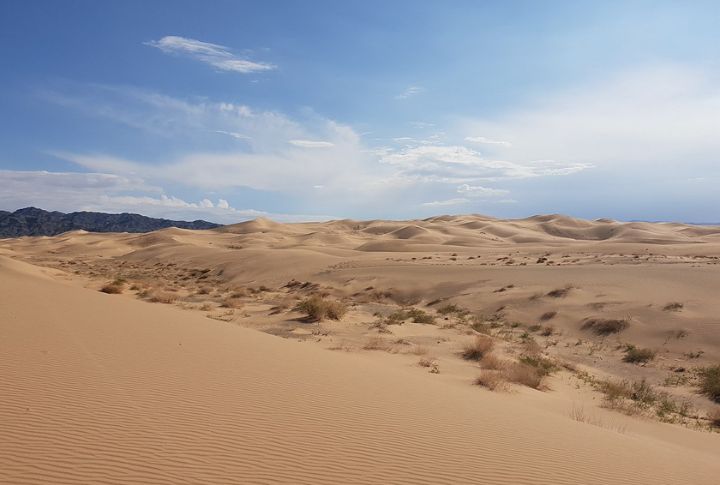

The Gobi Desert was once a lush environment known for its dinosaur fossils. Fossils of theropods, ancient mammals, and even dinosaur eggs offer insight into the diverse life forms during the Mesozoic era.
Dinosaur Ridge in Colorado
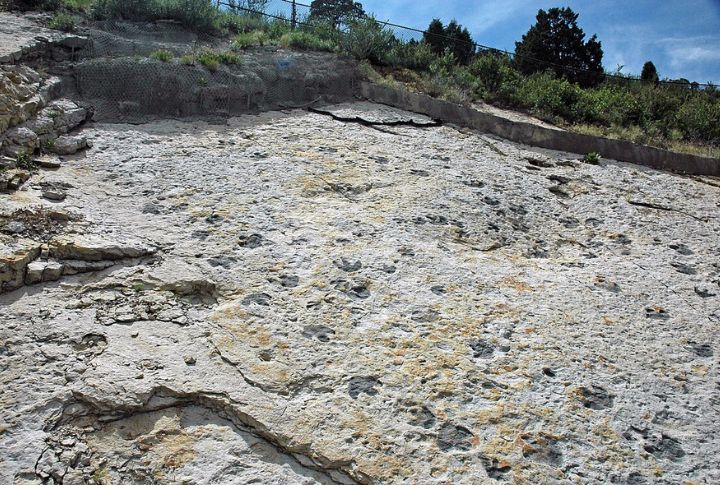

Dinosaur Ridge is home to one of the most extensive fossil trackways from the Late Jurassic period. Over 300 fossil tracks have been uncovered, offering detailed insights into how these prehistoric creatures moved.
Cape of Good Hope in South Africa

The fossils found at the Cape of Good Hope highlight the diversity of marine life, from ancient fish to marine reptiles. This site provides key evidence of the development of aquatic ecosystems and the evolution of life in Earth’s oceans over millions of years.
Baliem Valley in Papua New Guinea
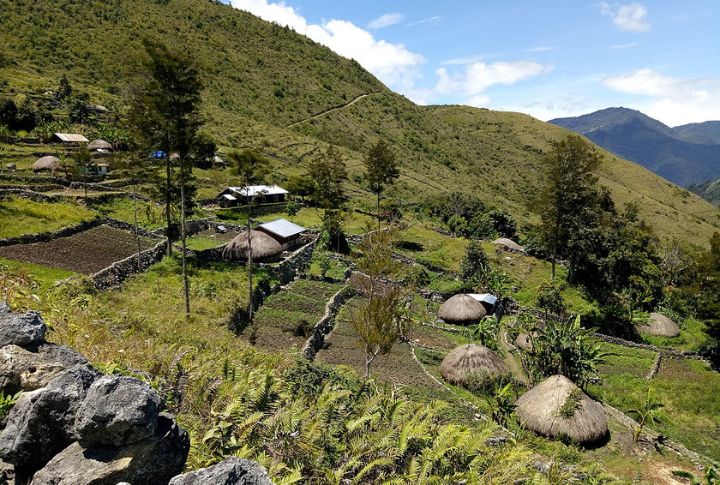

A relatively underexplored fossil site, the Baliem Valley, holds essential evidence of early human presence in Oceania. The fossils discovered here could help trace the migration patterns of Homo sapiens across the Pacific.
