Local
Is The Hispanic Population Driving Post-Pandemic America?
America’s population is shifting in ways that demand attention. With slower national growth and aging trends, one group continues to surge. These ten insights reveal how Hispanic communities are changing demographics, economics, and even politics in today’s post-pandemic United States.
Post-Pandemic Population Trends

The US experienced a slower population increase after COVID-19. Census data shows that the overall increase stagnated, except among Hispanic populations, which continued to rise. Reduced non-Hispanic birth rates and aging demographics further accelerated the Hispanic share of the total population.
Hispanic Population Growth In Numbers
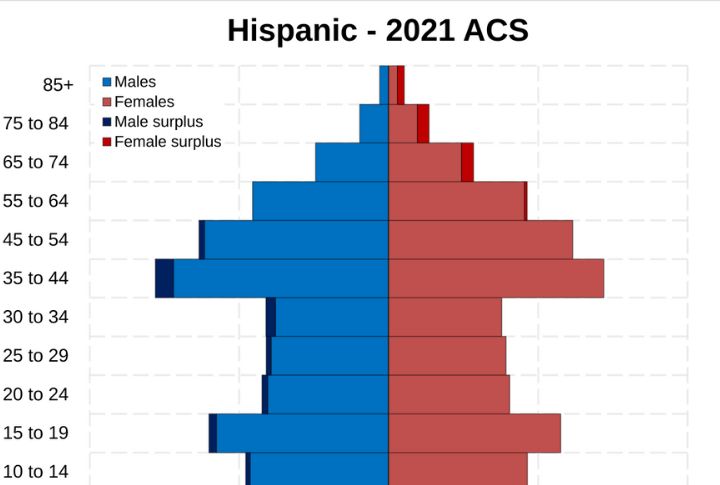
The Hispanic population in the United States reached approximately 65 million, accounting for 19.5% of the total US population. Between 2023 and 2024, the Hispanic community grew by about 1.16 million, which is nearly 71% of the nation’s total population increase during that period.
Major Contributors To Growth

Birth rates among Hispanic families remain significantly higher than those of non-Hispanic groups. The latest statistics show Hispanic fertility rates surpassing national averages, sustaining growth. Additionally, increased immigration, particularly from Latin America, bolsters these figures and ensures continued demographic influence in major metropolitan areas.
Geographic Hotspots
Urban centers and southern states are at the forefront of Hispanic population expansion. Texas, Arizona, Florida, and California saw the largest influx, while cities like Houston and Miami are showing rapid demographic shifts. These concentrations influence economic and social structures and make Hispanic communities integral to development.
Hispanic Influence On The Workforce

Hispanic workers now represent nearly 20% of the American labor force, and this number steadily rises. Their participation dominates industries such as the construction and service sectors. As older generations retire, this trend suggests that Hispanic workers will play an even larger role in sustaining economic stability.
Cultural And Economic Impact

Money spent by Hispanic consumers has experienced a remarkable hike, with buying power up 79% between 2014 and 2024, reaching an impressive $2.5 trillion. This substantial rise underscores the expanded economic footprint of Hispanic communities and highlights their integral role in America’s economic evolution.
Political And Electoral Implications

With an estimated 35 million eligible to vote in 2024, Hispanic voters are reshaping electoral dynamics, too. Analysts predict their growing numbers will influence policy discussions, particularly on immigration and economic reform. By 2030, their impact could redefine battleground states and national election outcomes.
Educational And Youth Demographics

Young Hispanics now constitute over a quarter of all K-12 students, and this marks a generational transformation. School enrollment data underscores this shift with nationwide bilingual education programs. As this population matures, the workforce and political representation will increasingly reflect Hispanic backgrounds.
Challenges And Barriers

Despite impressive growth in numbers, economic disparities persist, with Hispanic median household income trailing non-Hispanic white counterparts. Education gaps, lower homeownership rates, employment vulnerabilities, and other challenges limit upward mobility. Addressing these inequalities will determine whether Hispanic growth translates into broader economic equity.
Comparison With Other Demographics

As non-Hispanic white populations shrink, Black and Asian groups are experiencing modest increases. Hispanic expansion surpasses all other demographic categories, so this positions them as the growth engine. This shift challenges traditional majority-minority narratives and prompts adjustments in public policy.